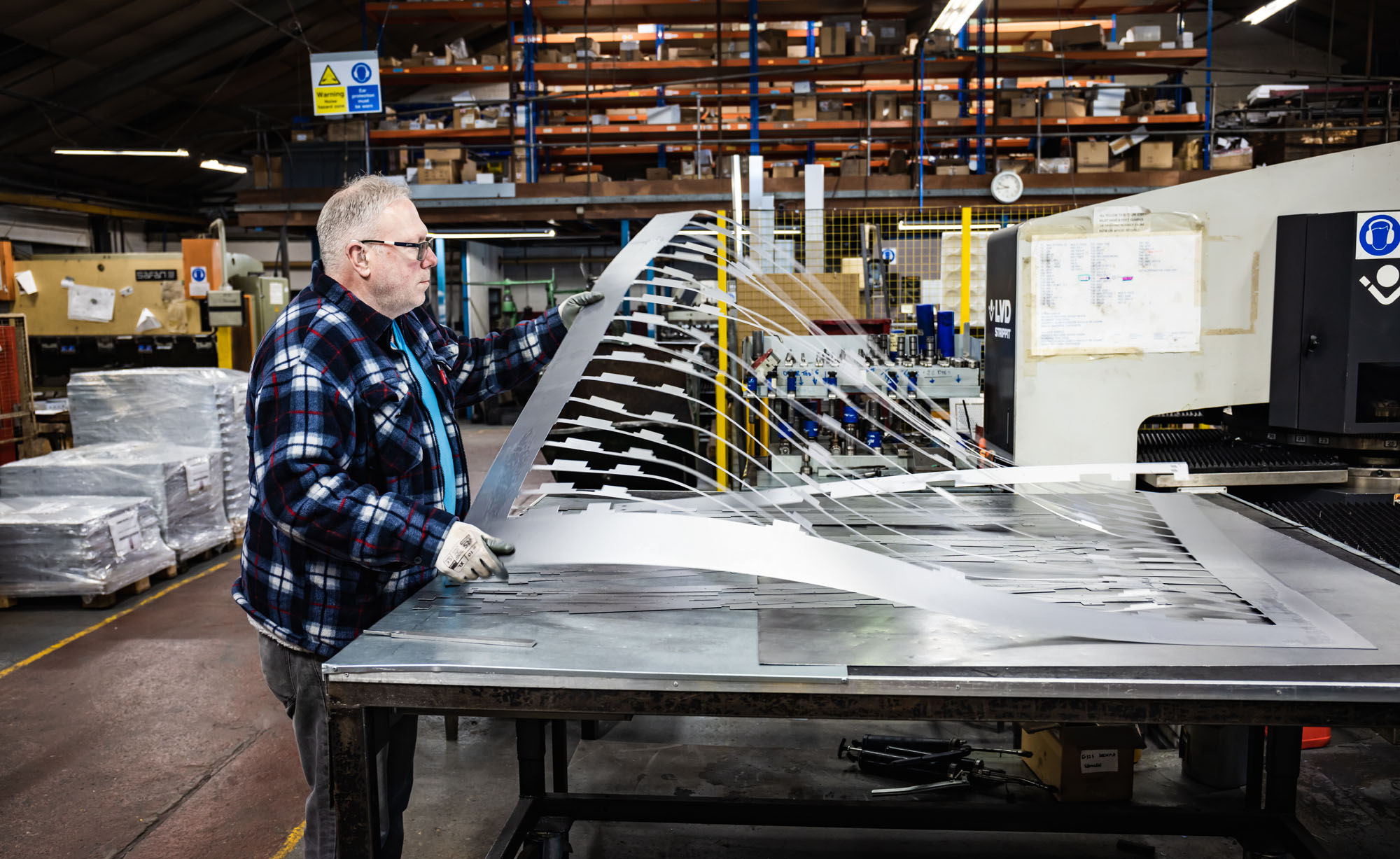
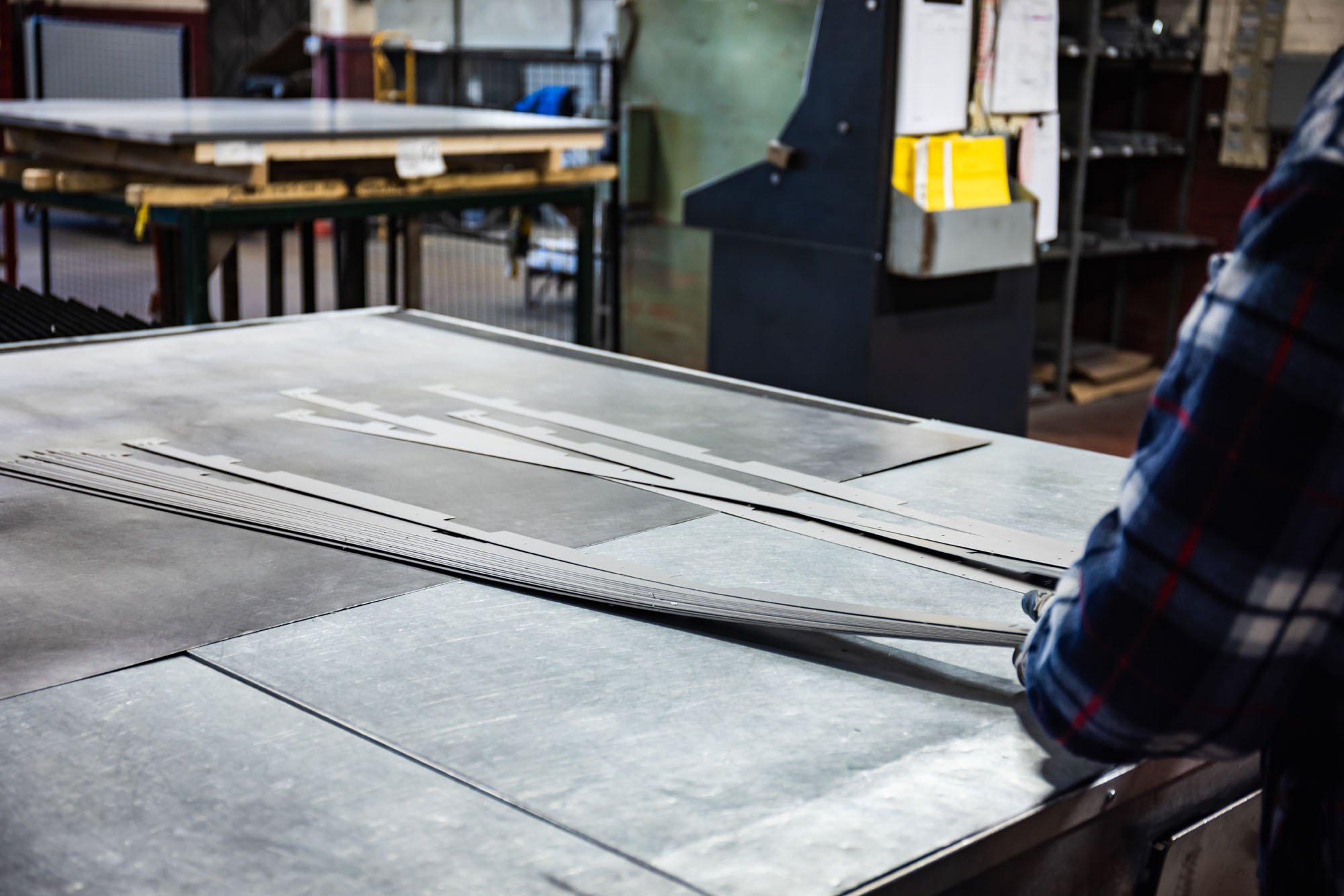
DC’S CNC punching facilities provide unmatched productivity, reliability, and flexibility, along with exceptional efficiency through automated “lights out” production.
Our unmanned CNC punching machines operate 24/7, resulting in significantly enhanced productivity and improved quality. Our customers benefit from unparalleled process consistency, setting new industry standards in punching.
We offer unbeatable speeds for various punching applications, including part number stamps, rib forming, special forms, countersinks, and more.